What is Linux KVM & Install KVM Virtual Machine
Complete Description – What is Linux KVM
What is Linux KVM Windows?
KVM stands for Kernel-based Virtual Machine, which is a complete virtualization solution for Linux kernel, which turns it into a hypervisor. Linux KVM virtualization was included in the mainline Linux kernel in version 2.6.20 and stable as well as fast for many workloads.
Features of KVM Linux
After Understanding about What is Linux KVM you must know its basic features. There are many useful advantages while using Linux KVM virtualization to deploy users virtual platform. There are following features those are mentioned below:
- Allocate Linux KVM Virtualization
It means to allocate more virtualized memory and CPUs in Linux rather than the available resources on the Computer system. - Optimizing Efficiency
It is capable of allocating the flexible storage and optimizes the available space for each guest virtual machine. - Disk I/O Requests
It provides the capability to set a range on the disk I/O and sent the request from the virtual machine to the host machines. - Automatic NUMA Balancing
It helps to improve the Linux KVM performance, which is running on NUMA hardware systems. - Capability of Virtual CPU
Provides the potential to increase the processing power as required on running Linux KVM virtual machine, without any downtime.
How to Install KVM and Create Linux KVM Virtual Machine on Linux
If users are using Linux, then, no need of VirtualBox or Vmware for creating virtual machines. Users allow to use the Kernel-based virtual machine to run for both Windows and Linux as well in virtual machines. Moreover, users are allowed to use KVM directly or with other command line tools. There are following points which help to install, Create and manage Linux KVM virtualization using commands in Linux platform those are discussed below:
Installation of Linux Virtual Machine
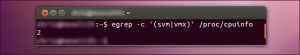
KVM only works if users CPU has a support for hardware virtualization either using Intel VT-x or AMD-V. Determining whether users CPU, which includes such features and run the following command as shown in the screen-shot:
![]()
For example- Zero(0) indicates that users CPU unable to support hardware virtualization whereas one (1) or more signifies that it does. Users must have to enable hardware virtualization support in users PCs BIOS, although if this command returns the output as one(1) or more.
Use the above command to install Kernel Linux KVM Virtual Machine and supporting packages. Virt-Manager is a graphical application helps to handle users virtual machine also, users allow to use the KVM command directly. But still, libvirt and Virt-Manager command simplify the process.
![]()
Only the root user and users available in libvirt group have a permission for utilizing the Linux KVM virtual machine. Run the given command to add users account to the libvirt group:
![]()
After performing this command, log out and log back in. Now, run this command again after back log in and users must view a free list of virtual machines. This will help to indicate that everything is working properly.
![]()
Create Linux KVM Virtual Machine
Once users have finished the KVM installation, the easiest way to utilize it with Virtual Machine Manager application. A user will find it in their dashboard.
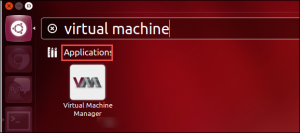
Click on Create New Virtual Machine option on the toolbar and then, the Virtual Machine Manager will configure users virtual machine details and installing users guest operating system according to their choice to deploy Linux KVM virtualization.
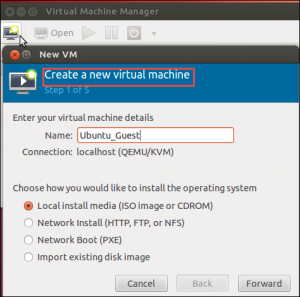
The procedure will be well-known if users have used VirtualBox, VMware, or other virtual machine application. Users must install from a hard disk, ISO image or even a network location.
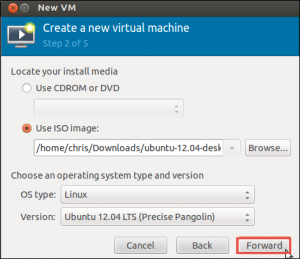
Now, assigning more than 2GB of memory to a virtual machine, users will want a 64-bit Linux kernel. In fact, systems can run 32-bit kernels and able to assign maximum 2GB RAM to a Virtual Machine.
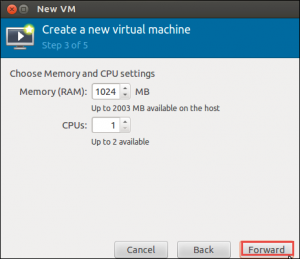
KVM provides NAT-like bridged networking by default. Users, Linux KVM virtual machine cannot appear on the network as its own device but have the capability of accessing the network through host operating system. If users are running server application in virtual Machine and want to accessible from other devices on the desired network, users will have to change the network settings.
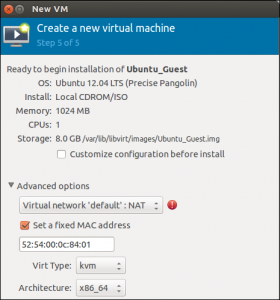
After determining users installation method, Virt-Manager will boot the guest OS in Windows. Now, install the guest operating system as users want on a physical machine.
Manage Linux KVM Virtual Machine
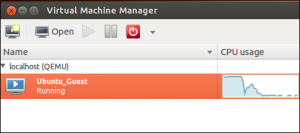
Now, the Virtual Machine Manager Windows will show a list of users installed virtual machines. After that, clicking right on a virtual machine in the Windows for performing the actions, which includes starting, shut down, cloning or migrating them.
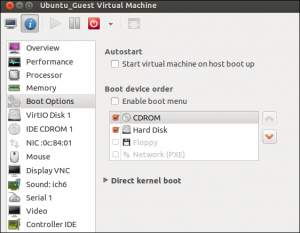
Finally, users able to view the information about the Linux KVM virtual machine and also, configure its virtual hardware by selecting I-shaped toolbar option in the virtual machine’s Window to deploy Linux KVM virtualization.
Conclusion
KVM is a free, open source virtualization infrastructure for Linux kernel distribution. Also, it has been ported in the form of loadable kernel modules. Moreover, in the above section, we have discussed What is Linux KVM & information related to Linux KVM Virtualization and its features. Also, we have mentioned a procedure how to install, create and manage KVM virtual machine command line in detail.

