What is RAID Disk Storage Standard & Non-Standard Levels
Learn What is RAID Technology
What is RAID Technology? The term RAID was defined as a Redundant Array of Independent/Inexpensive Disks. It is the way of data storage visualization technology to combine several physical disk drive components into a single logical unit for the purpose of providing fault tolerance, increasing the storage capacity and improving the performance as well. Moreover, the data is distributed over the drives in multiple ways, known as RAID levels, which depends on redundancy and performance level. RAID disk drives are frequently used on servers site but are not essential for personal system. In the following section, we will discuss what is RAID Technology standard or non-standard levels and RAID storage techniques.
RAID Storage Disk Technology
The major methods of saving data in the same array by using latest developments RAID technology. The following points are mentioned below that you need to understand to know the concept of what is RAID Technology:
- Striping
A splitting technique for spreading the flow of each data across multiple disk drives. Also, RAID offers the option of reading or writing more than one disk at the same time in order to affect on improving the performance.
- Mirroring
It is a storage technique in which the identical copies of one or more disks in the same array, so that if one disk gets fail then, the data are simultaneously preserved on the RAID members. This type of data arrangement impacts the fault tolerance and the performance.
- Parity
This technique is used in striping and checksum methods. In this arrangement, a certain parity function is calculated for data blocks into segments. In any case, if the drive becomes fail, the missed blocks are recalculated from checksum approach and provides the RAID fault tolerance.
Types of Multiple RAID Levels
Standard RAID Levels
What is RAID Standard LEVEL: RAID devices are different schema or layout of data distribution, known as RAIDs which provides reliability, performance, availability and capacity. RAID levels tell how data is distributed across the disk drives. Standard RAID levels including the various points:
- RAID 0: Striping Disk Array
Standard RAID level 0 – Provides data spreading out blocks of each file over multiple disk drives without any redundancy. This will help to improve the performance but unable to deliver fault tolerance. In any case, if a single drive fails 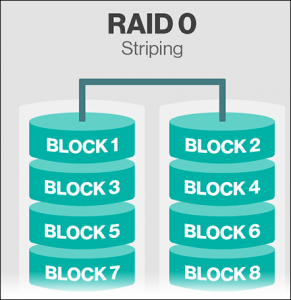 then, all the data in the disk array is lost.
then, all the data in the disk array is lost.
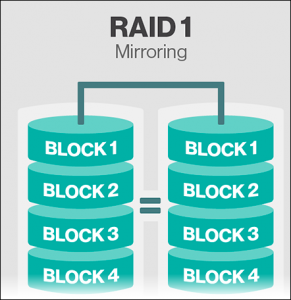
- RAID 1: Utilize Mirroring and Duplexing
Standard RAID level 1 – Provides variation in data mirroring without striping or parity. This configuration consists of two drives which store the duplicate data. Read performance has improved either data can be read transaction rate at the same time. Write transaction rate as for single disk storage.
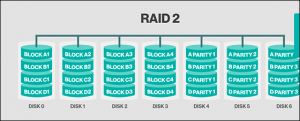
- RAID 2: Error-correcting code
Standard RAID level 2 – This configuration has used stripping over disks with some disk storage error checking and then, correcting the information properly. It marks data at the bit RAID rather than block RAID. It has not implemented accurately and is rarely used.
- RAID 3: Parity Bit-interleaved
Standard RAID level 3 – This technique provides byte level striping RAID and dedicates a single drive to store parity disk information. RAID 3 can not provide service on multiple requests simultaneously and unable to overlap Input/Output. Due to this reason, RAID 3 is best for single-user systems along with long record application.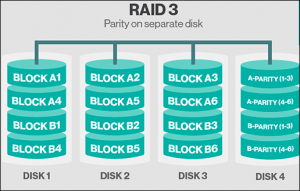
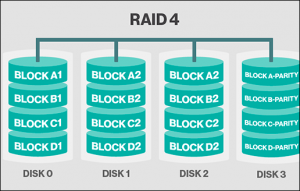
- RAID 4: Dedicated Parity Drive
Standard RAID level 4 – This RAID is commonly used for implementation of RAID, which provides block-RAID striping records (like level 0) with a parity disk. If a data disk gets fail, the parity drive is used for creating a replacement disk. A disadvantage of this RAID is that the parity disk creates write bottlenecks instead of read.
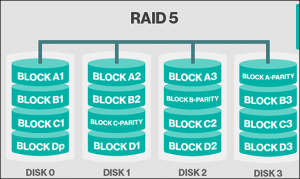
- RAID 5: Block interleaved distributed parity-bit
Standard RAID level 5 – Provides data striping at the byte level and also describe stripe error correction information. As the results in amazing performance and fault tolerance. Level 5 is one of the most popular implementations of RAID.
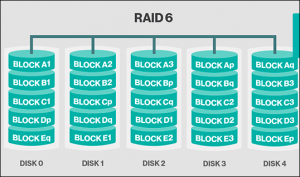
- RAID 6: Independent data with double parity
Standard RAID level 6 – RAID 6 provides of block-level striping with double distributed parity data across all disks. Double parity gives fault tolerance up to 2 failed disk drives.
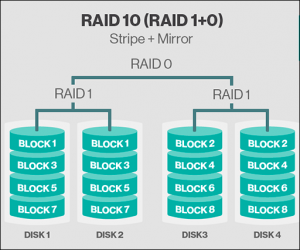
- RAID 10: Combining (RAID 1+0)
Standard RAID levels – Not only one original RAID levels, even multiple RAID 1, as well as RAID 0 mirrors are created.
Non-Standard RAID Levels
Several devices can use more than one RAID level in a hybrid or nested arrangement, and few vendors offer non-standard proprietary levels. The following examples of non-standard RAID levels are:
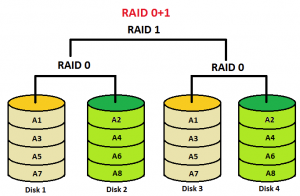
- RAID 0+1: Add Level (0+1)
Non-Standard RAID levels – Combining RAID 1 and RAID 0 this RAID is referred as RAID 10 stripes, which offers the high performance. In RAID 1+0, the data mirror is created and reflects are striped. Used for both replicating and sharing data across disks.
- RAID 7
Non-Standard RAID level 7 – This RAID level is dependent on levels 3 or 4 but adding cache to the mix. It has considered a real-time embedded OS as a controller, caching through the high-speed bus and other characteristics of the system.
- RAID 1E
Non-Standard RAID level 1E – A RAID 1 implies with more than two disks. Data splitting is combined with mirroring each written stripe to one of the remaining disks in the array.
- RAID S
Non-Standard RAID level S – Also known as Parity RAID, this is an alternate method for striped parity RAID from EMC Corporation’s used in Symmetrix storage systems that are no longer used on current equipment.
Conclusion
RAID is a disk which provides a way to store the common data in different places on multiple hard disks. Understanding the various aspects of the hard disk, we have presented the entire information to let the users understand what is RAID Technology i.e., redundant array of independent disks and its technologies and RAID levels in details. Also, we have discussed standard and non standard RAID levels.

